Locked Traslation Memory entries can be created in several ways:
1- Following properties are set to
true in tm.properties file (the default value is 'false'):
enable_auto_segment_lock_on_locked_spice_match=true
enable_auto_segment_lock_on_locked_ice_match=true
enable_auto_segment_lock_on_locked_ice_asset_match=true
2- A
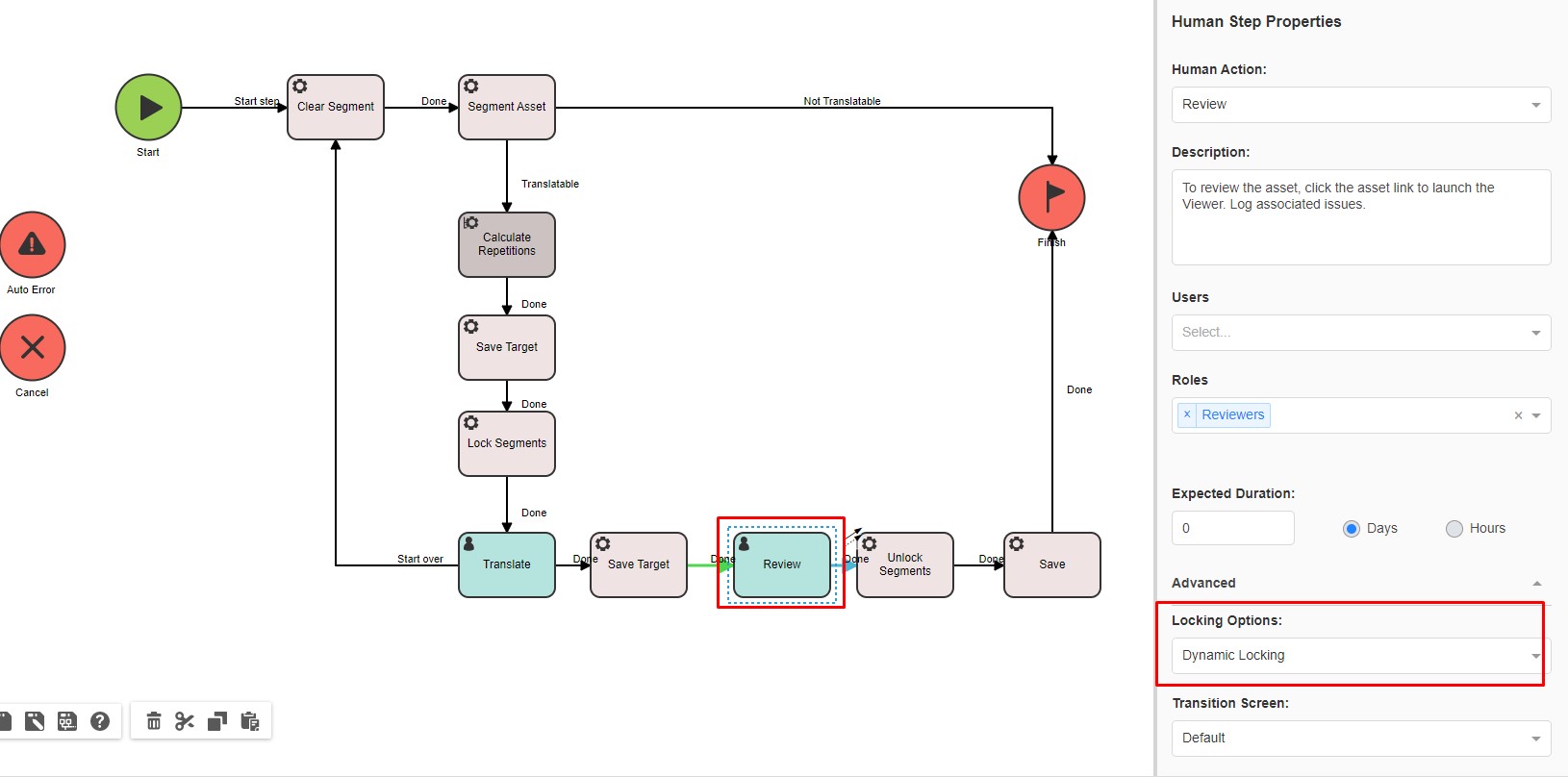
Lock Segments Automatic Step that locks segments with a certain segment status is used in the Workflow.
Note: this would only work
if the relevant properties in tm.properties are set to
true (see #1). If they are set to
false, the TM entries will not be locked
3- A manual change in the Translation Memory: a user edits TM entries manually and locking them directly in the TM via
Tools > TMs > [TM] > [TM Entry]4- A Studio Return package that contains locked segments is imported and the TM is updated with those segments.
Note: this would only work
if the relevant properties in tm.properties are set to
true (see #1). If they are set to
false, the TM entries will not be locked
5- A user locks a segment in Browser Workbench. Note: this is only possible if the human step (i.e
Review) has
Dynamic Locking enabled.
Locking can be set to
dynamic or static in the
Advanced setting of the human step.
Dynamic locking means that this user can change the status of a locked segment and unlock it or lock it again as required.
The
dynamic locking is usually applied to the
Review step to allow Reviewers to make changes in the translation when required.
The
static locking means that the user assigned to this step
cannot change the status of locked segments. He/she can only view the locked segments or add a comment. The static locking is usually applied to the
Translate step and prevents translators to change segments that have already been reviewed.